Matlab Read a Row Where Column Value Equal

If y'all look at the MATLAB, Vector and Matrix are ii basic fundamentals components. And then, nosotros need to become familiar with the matrix, vector, how to generate them, different MATLAB matrix operations and functions…
In the last tutorial, I described the MATLAB Vector with their functions and mathematical manipulations on the MATLAB command window.
Let's beginning this complete tutorial about MATLAB matrix operations.
Table of Content:
- Introduction about the Matrix in MATLAB
- Creating and Generating the Matrix in MATLAB
- Transpos of the Matrix
- Determinant of the Matrix
- Inverse of the Matrix
- MATLAB Matrix Operation
- Matrix Functions in MATLAB
-
- Getting all Diagonal Elements of the Matrix
- Finding out Eigenvalue of the Matrix
- Determining the Rank of the Matrix
- Creating a Zero Matrix
- Generating an Identity Matrix
- Creating a Ones Matrix
- Finding a Size of the Matrix
INTRODUCTION
The definition of the Matrix is a two-dimensional array which consists of both the rows and columns.
In the MATLAB matrix, the rows and columns are created by using the commas (,) /line-spaces ( ) and semicolon (;) respectively.
The matric is represented by thesquare brackets '[ ]'.
Creating and Generating the Matrix in MATLAB
In the generation of the matrix department, nosotros are studying 'How to create the Matrix [Rows and Columns] in MATLAB?'.
The terminal tutorials I shared 'How to create the vector in MATLAB?'. This tutorial is well-nigh creating the Matrix rows and columns with the detail explanation.
For creating MATLAB Matrix, you must have four points to recollect.
- Start with the open square bracket '['
- Create the rows in the matrix past using the commas (,) or line-spaces ( )
- Create the columns in the matrix by using the semi-colon( ; )
- End with the close square bracket ']'
Permit'southward look at the full general representation of matrix with the row and column…
The general representation of Row Matrix is…
A = [x1, x2, x3, ....... xn] or [x1 x2 x3 ....... xn] This is (1 × north) vector i.e. a single row consisting the n th term elements.
The general representation of Column Matrix is…
A = [x1; x2; x3; ....... xm] This is (1000 × 1) vector i.e. a single row consisting the m th term elements.
Note: Row matrix and column matrix are nix merely the vectors.
For example,
How to generate or create North×M Matrix in MATLAB?
Solution: The iii×3 matrix must have 3 rows and iii columns. These rows and columns are created with the assistance of space and semicolon.
The matrix in MATLAB:
>> Matrix A is...>> A= [2 3 three; 1 2 viii; 7 9 iii]
A =
two three 3
1 2 viii
vii nine 3
The output on MATLAB Window:
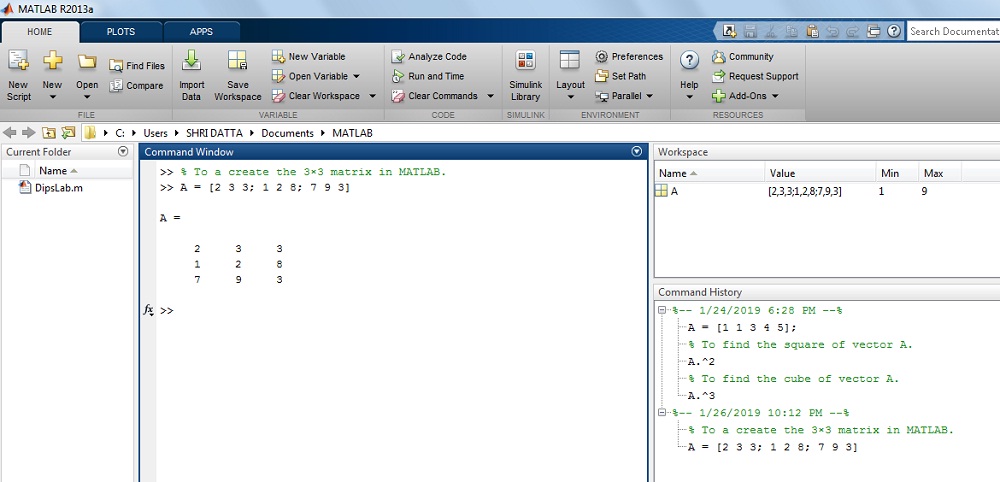
In this section, nosotros have seen how to create and generate the matrix.
Moving to the next part…
TRANSPOSING OF MATRIX
What is the Transpose of the Matrix?
Transpose method is a mathematical functioning where…
- The elements of the row are converted into the elements of the column. (or)
- The elements of the column are converted into the elements of the row.
The transpose of the Matrix is represented by an apostrophe or single quote (') or power of T like as [ ]' 0r [ ]T.
Note: The representation of the transpose of the Matrix is the same as the representation of the transpose of the vector.
Here is a general syntax for Transpose of the Matrix.
Transpose of matrix A (A') is
A = [x1 x2 x3; x4 x5 x6; x7 x8 x9]'= [x1 x4 x7; x2 x5 x8; x3 x6 x9]
Transpose of matrix B (B') is
B = [x1 x4 x7; x2 x5 x8; x3 x6 x9]' = [x1 x2 x3; x4 x5 x6; x7 x8 x9]
If yous perform transpose performance twice on the matrix, it volition give the same matrix.
i.eastward.
A = (A')'
Let's accept a mathematics instance…
How to determine the transpose of the given below matrix D?
where D = [2 0 i; 9 6 8; four 1 1]
Solution: You tin can use the transpose method to change the row vector into a column vector.
>> D =
2 0 1nine 6 8
4 i ane
>> By using the transpose method,
>> D' =
2 ix 40 6 1
i viii one
The output on the MATLAB Window:
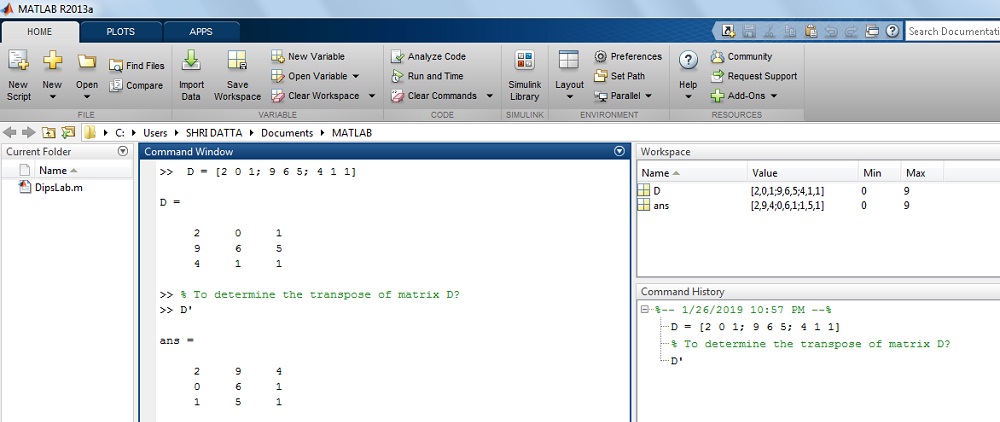
Looks similar its pretty simple till now. Isn't information technology?
DETERMINANT OF MATRIX
What is a determinant of the Matrix?
It is a special number calculated from the square matrix. If you are not aware of determinant if the matrix, you lot tin can check here.
Note: Yous tin can calculate the matrix determinant merely where if it is square matrix ways the number of rows and the number of columns will be the same.
In MATLAB, we can easily make up one's mind the 'Determinant of Matrix' by using the 'det' function. You don't need to do any mathematical operation explicitly.
The general Syntax is,
x = det(10) Return the determinant of matrix '10'Where, x is matrix.
Example,
How to find the determinate of matrix 'P' in MATLAB?
Where, P = [ane 5 3; 1 2 nine; 7 eight 5]
Solution: The given value of matrix 'P' is
>> P = [1 v 3; 1 2 9; 7 8 five]
>> P =i five 3
1 two 9
vii 8 5
>> det(P)
ans =
210.0000
The output on MATLAB Window:
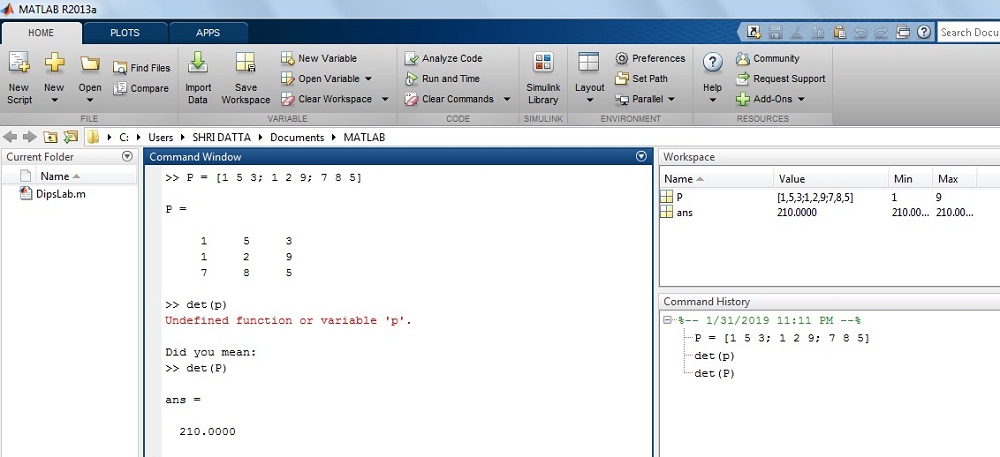
Inverse OF MATRIX
What is Inverse of the Matrix?
If the multiplication of the matrix A and matrix B is the Identity matrix, matrix B is the inverse of matrix A.
If you lot are interested to know how to summate the inverse of matrix mathematically, cheque this link.
In MATLAB, the inverse of the matrix is calculating by using the 'inv' office. The representation of inverse matrix is 'matrix ability of -1' or []-ane
The general Syntax is…
x = inv(x) Return the inverse value of matrix 'ten'Where, x is matrix.
Example.
How to summate the inverse of the matrix 1000 in MATLAB?
Where, M=[ane two two; 9 vii 6; five 4 6]
Solution: By using the inverse part,
>> M=[i 2 2; 9 seven half-dozen; v 4 half-dozen]>> G=
ane 2 2
9 seven six
five 4 6
>> inv(M)
ans =
-0.6429 0.1429 0.0714
0.8571 0.1429 -0.4286
-0.0357 -0.2143 0.3929
The output on MATLAB Window:
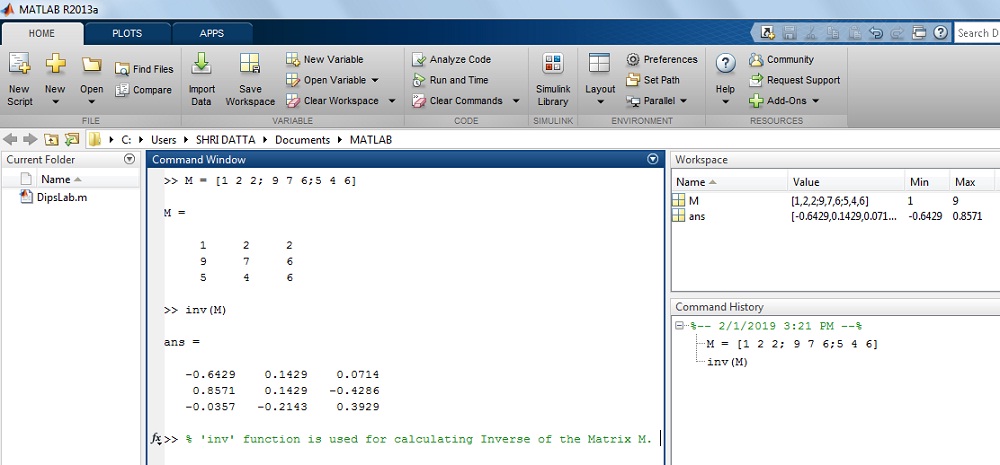
This is all well-nigh a simple function to calculate the inverse of the matrix in MATLAB.
MATLAB MATRIX OPERATIONS [Mathematical]
Earlier we accept seen the different types of mathematical functions and their short abbreviations. In this section, we volition perform same mathematical operations on Matrix.
In the MATLAB environment, the mathematical operations (functions) on Matrix are the same as Vector.
What are the unlike mathematical operations nosotros can perform on the matrix in MATLAB?
| Mathematical Arithmetics Performance | Notation andSyntax for Matrix |
| Improver | + |
| Subtraction | – |
| Multiplication | .* |
| Sectionalization | ./ |
| Exponential or power | .^ |
MATRIX FUNCTIONS in MATLAB
The MATLAB provides the various functions for mathematical matrix manipulation.
Nosotros will encounter those MATLAB matrix functions one by one…
1. How to notice Diagonal element of the Matrix in MATLAB?
In the MATLAB command window, 'diag' syntax is used to become the diagonal elements of the matrix.
The general Syntax:
x = diag(x) Return the diagonal value of matrix '10'Where, x is matrix.
Case
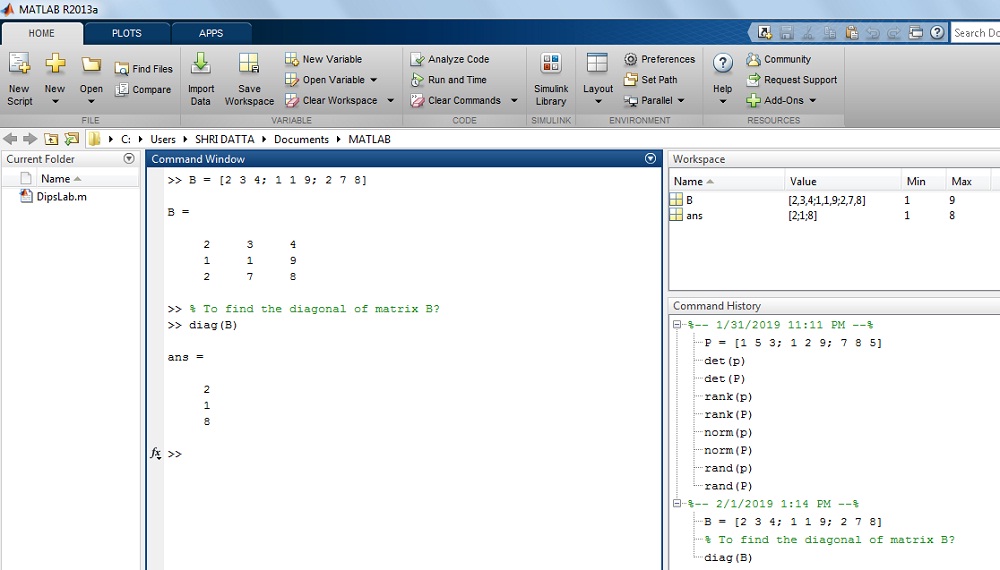
How to get all the diagonal elements of Matrix B in MATLAB?
Where, B = [ii three iv; ane one 9; 2 7 8]
Solution: The given value of matrix B is
>> B = [ii 3 4; 1 1 ix; two 7 8]>> B =
two three 4
1 one 9
2 seven 8
>> diag(B)
ans =
2
1
8
The result on MATLAB display:
2. How to determine the Eigen-value of the Matrix in MATLAB?
What is Eigen-Value of Matrix and how to calculate information technology?
Note: This video is just for your understanding. You don't demand to practice any mathematical operations to find the eigenvalue of the matrix in MATLAB.
In MATLAB, it is pretty easy.
The eigenvalue of the matrix calculated by using the 'eig' syntax in MATLAB.
The general Syntax is,
x = eig(10) Render the eigen value of matrix 'x'Where, x is matrix.
Example.
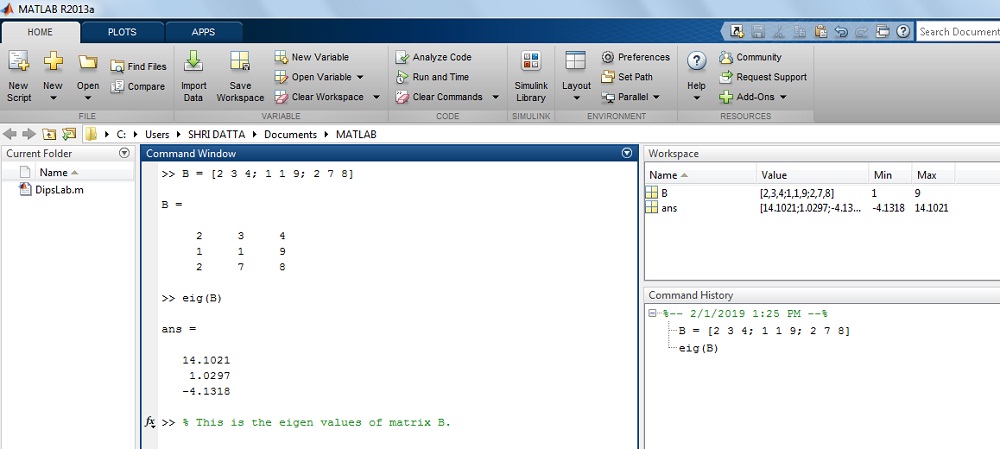
How to notice the eigenvalue of Matrix B in MATLAB?
Where, B = [two 3 4; 1 1 9; 2 seven viii]
Solution:
>> B = [2 3 4; 1 1 9; two 7 8]>> B =
ii 3 4
i 1 9
2 7 viii
ans =14.1021
ane.0297
-iv.1318
The consequence on MATLAB display:
3. How to notice the Rank of the Matrix in MATLAB?
What is the rank of the matrix?
The rank of a matrix is divers equally the maximum number of linearly independent column vectors in the matrix. Information technology is similar to the maximum number of linearly independent row vectors in the given matrix.
Here is video if yous are interested in finding rank of the matrix in general.
In MATLAB to detect the Rank matrix,'rank' office is used.
The full general Syntax is..
x = rank(ten) Return the rank of matrix '10'Where, x is matrix.
Example.
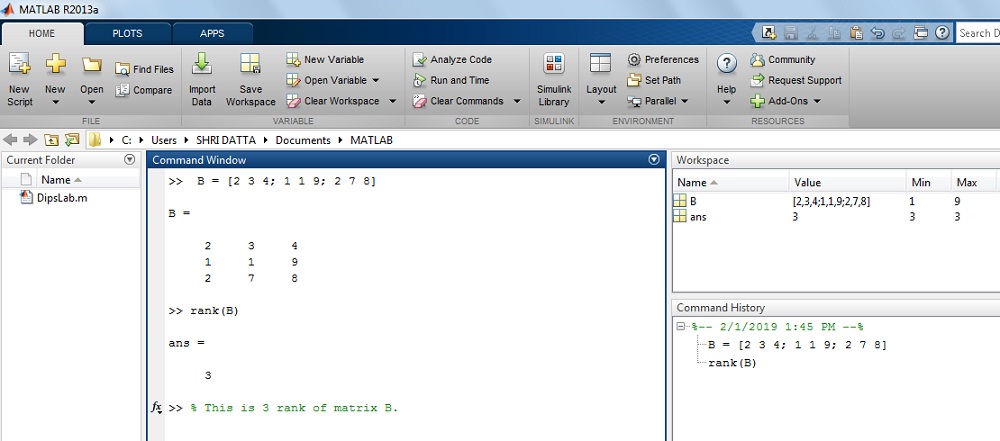
How to detect out the rank of Matrix B in MATLAB?
Where, B = [2 3 4; 1 ane ix; 2 7 8]
Solution: For the given matrix B,
>> B = [two 3 iv; 1 1 ix; two 7 8]>> B =
2 three 4
1 ane ix
2 7 8
>>rank(B)
ans =
three
The upshot on MATLAB brandish:
four. How to create Null Matrix using zeros function in MATLAB?
What is Cipher Matrix?
In the nada matrix, all the elements of the matrix are zero.
In the case of MATLAB, zeros function is used to create all zero in rows and columns of the matrix.
The general Syntax is…
x = zeros(x) Return the zeros of matrix 'x'Where, x is matrix.
Example.
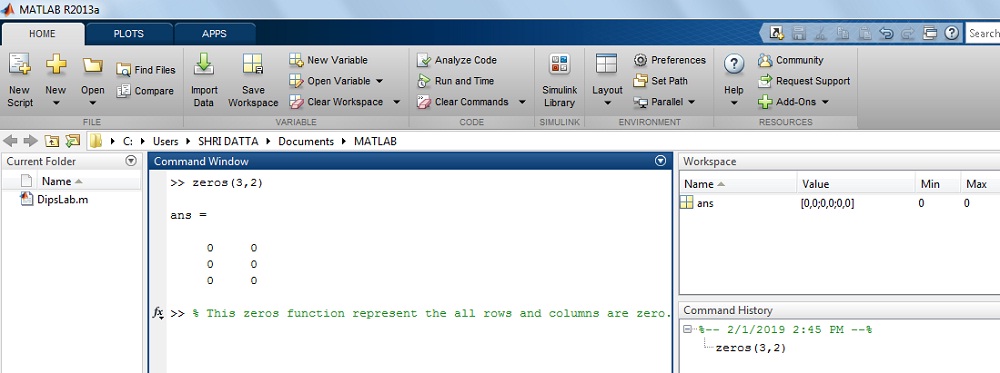
How to create a zero matrix in MATLAB?
Where, matrix A is 3 by 2 matrix,
Solution: The matrix A is
>> A= zeros(three,2)ans =
0 0
0 0
0 0
The event on MATLAB brandish:
5. How to create Identity matrix using centre Function in MATLAB?
The optics function in MATLAB is used to create the identity matrix.
The general Syntax is…
x = eye(x) Render the eye of matrix 'x'Where, x is matrix.
Example.
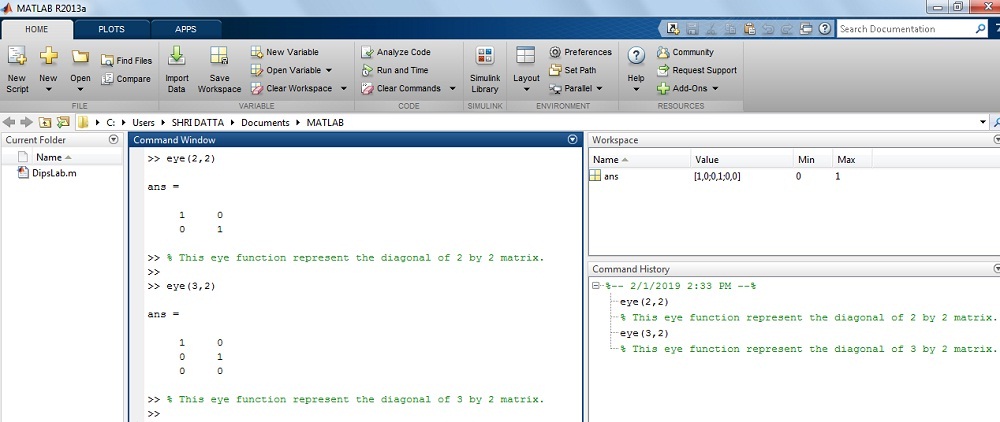
How to generate the Identify Matrix by using the eye role in MATLAB?
Where matrix A is 2 by two matrix.
Solution: The matrix A is…
>> centre(2,2)ans =
i 0
0 1
The result on MATLAB display:
half dozen. How to create Matrix with all elements every bit i using ones part in MATLAB
In MATLAB, the 'ones' function is useful for creating the matrix with all elements 1.
The general Syntax is…
ten = ones(a) Return the ones of matrix 'x'Where, 'a' is a size of the matrix
Case.
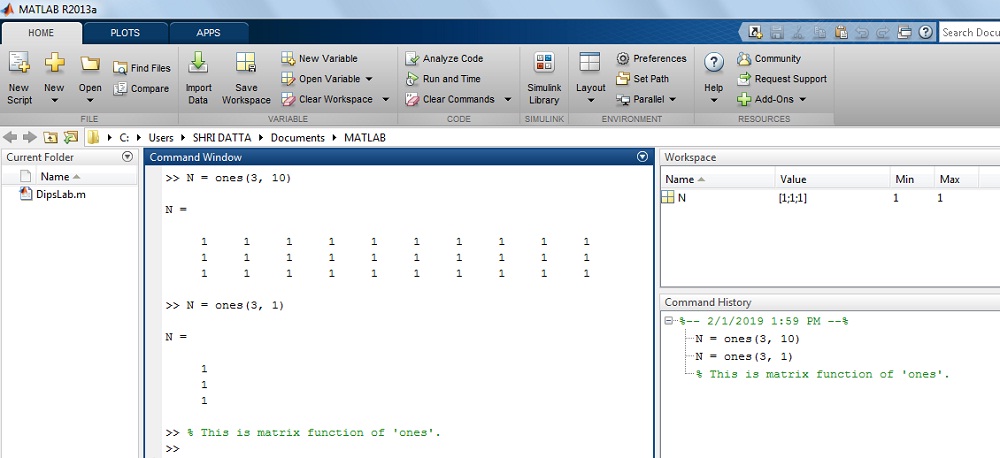
How to generate the matrix with all elements i in MATLAB?
Where, matrix A is ii by 2.
Solution:
>> A = ones(2)ans =
1 1
1 1
Or
>> North = ones(3,1)
N =
1
1
1
The effect on MATLAB display:
seven. How to find the size of the matrix in MATLAB?
In MATLAB, we tin can notice out the number of columns and rows with the help of 'size' function.
The full general Syntax is,
south = size(x) Return the size of matrix 'x'Where, ten is matrix.
Example,
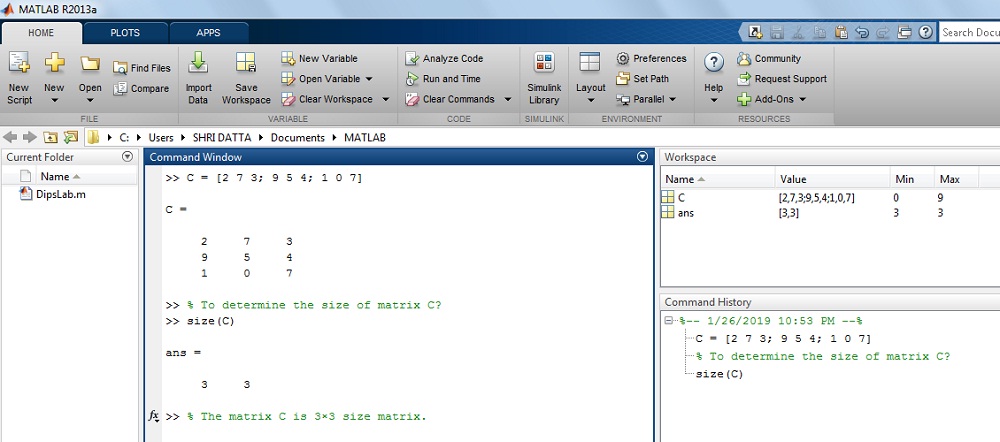
How to determine the size of matrix C in MATLAB?
Where, C = [2 seven iii; 9 5 4; 1 0 7]
Solution: The given value of matrix C,
>> C = [two 7 iii; 9 v 4; ane 0 seven]>> C =
2 vii 3
9 5 4
1 0 vii
>> size(C)
ans =
3 3
The upshot on MATLAB brandish:
On this Matrix MATLAB tutorial, I tied my best covering all the basics of the matrix. And likewise explained mathematical operations and functions of the matrix by solving examples on the control window of MATLAB Software.
Bank check my all other MATLAB tutorials and keep exploring. I will be sharing more of such tutorials, stay tuned.
If you accept any query related to different MATLAB matrix operations, experience free to ask by commenting beneath. If you like this tutorial please comment your feedback and too share it with your friends and students.
I have completed master in Electrical Power System. I work and write technical tutorials on the PLC, MATLAB programming, and Electric on DipsLab.com portal.
Sharing my knowledge on this blog makes me happy. And sometimes I delve in Python programming.
Matlab Read a Row Where Column Value Equal
Source: https://dipslab.com/create-matlab-matrix-operations-functions/
0 Response to "Matlab Read a Row Where Column Value Equal"
Post a Comment